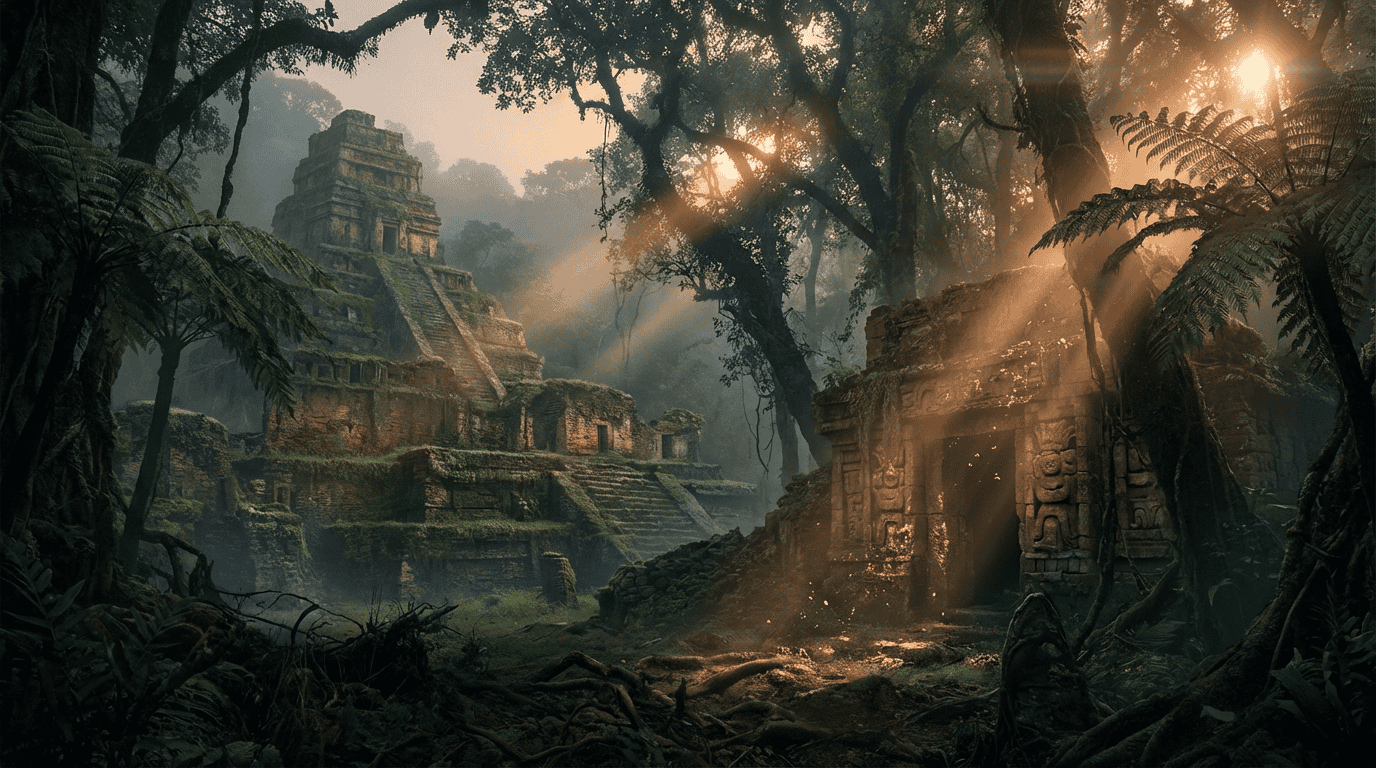
The Lost City of El Dorado: From Myth to Modern Discovery
For centuries, explorers risked their lives chasing a shimmering mirage deep within the South American jungle. The legend of El Dorado paints a picture of a magnificent city paved with gold and overflowing with unimaginable riches. Yet the reality of the Amazon rainforest proved far more dangerous and dense than these golden dreams ever suggested. Adventurers hacked through thick vines and faced deadly wildlife while hoping to find the glint of treasure behind the trees. Instead of a kingdom of metal, the jungle guarded secrets that are only just beginning to come to light through modern technology.
The story began with the Muisca people of Colombia and a sacred ritual rather than a physical city. Historical records describe a tribal leader who covered himself in gold dust before making offerings in the waters of Lake Guatavita. Spanish conquistadors heard these tales and misunderstood the ceremony as proof of a vast metropolitan empire built entirely of gold. This confusion sparked a frantic rush that led to the draining of the lake and countless failed expeditions. While they found some artifacts, the true wealth of the region remained hidden beneath the canopy for hundreds of years.
New discoveries in 2025 turned the page on this ancient mystery using advanced LiDAR technology. Researchers stripped away the digital layer of trees to reveal a complex network of settlements instead of a single golden metropolis. The scans expose engineered roads, ceremonial plazas, and geometric mounds that connect over twenty major sites. It appears the real treasure was a sophisticated society capable of thriving in one of the harshest environments on Earth. This revelation suggests that the legend was based on a powerful civilization that simply looked different than what the Europeans expected.
Key Takeaways
- The legend of El Dorado originated from a Muisca ritual involving a chieftain covered in gold dust, rather than a physical city paved with riches.
- Spanish conquistadors misunderstood indigenous accounts of the ‘Golden One,’ sparking centuries of futile attempts to drain Lake Guatavita and search the jungle for a non-existent metropolis.
- Advanced LiDAR technology has recently revealed a vast network of sophisticated ancient settlements and engineered infrastructure hidden beneath the Amazon canopy.
- The true treasure of the region proved to be a complex pre-Columbian civilization capable of thriving in the jungle, rather than the material wealth sought by explorers.
The Golden Man and Lake Guatavita
Deep in the Andes mountains of present-day Colombia, a ceremony took place that sparked one of history’s greatest obsessions. The Muisca people gathered at the edge of the sacred Lake Guatavita to watch their new leader initiate his rule. According to historical accounts, the chieftain was stripped naked and coated in a sticky substance before being covered entirely in gold dust. He stood on a raft like a glittering statue, shimmering in the sunlight as he drifted toward the center of the water. This figure was the true El Dorado, which translates simply to “The Golden One,” rather than a city of buildings and streets.
Once the raft reached the middle of the lake, the golden king would plunge into the frigid depths to wash away his wealth. Attendants and spectators threw piles of gold trinkets and precious emeralds into the water as offerings to their gods. When Spanish explorers heard rumors of this event, their imaginations ran wild with dreams of endless riches. They misunderstood the indigenous stories and assumed the gold dust came from a place where gold was as common as dirt. This misunderstanding transformed a specific cultural ritual into the enduring myth of a massive city paved with gold.
Treasure hunters have spent centuries trying to reclaim the riches resting at the bottom of Lake Guatavita. Early attempts in the 16th century involved trying to drain the lake, which revealed a handful of gold artifacts that confirmed the ritual was real. However, the water levels never dropped enough to expose the center where the greatest concentration of offerings would lie. While modern laws now protect the site from looters, many wonder if a massive fortune still waits beneath the mud. The legend of the Golden Man persists because it is rooted in fact, even if the city itself remains elusive.
Conquistadors and the Quest for Gold

The legend began not with a city of stone, but with a single man covered in shimmering dust. Indigenous stories from the Muisca people described a ritual where a new chieftain coated himself in sticky resin and gold dust before entering Lake Guatavita. Spanish explorers heard these whispers and immediately let their imaginations run wild with visions of vast riches. Instead of understanding this as a sacred ceremony, the conquistadors convinced themselves that a literal city built entirely of solid gold was waiting to be found. This error sparked a gold fever that would consume the lives and fortunes of many European adventurers for generations.
Desperate to claim this sunken treasure, explorers went to extreme lengths to empty the sacred waters of Lake Guatavita. In the late 16th century, a merchant named Antonio de Sepúlveda cut a notch into the lake’s rim to drain the water level significantly. Workers found a handful of gold trinkets and emeralds in the mud, which only fueled the belief that a massive hoard lay deeper at the bottom. However, the walls of the cut eventually collapsed and killed many laborers, forcing the Spanish to abandon the dangerous project empty-handed. Despite finding only small clues, the failure did little to stop the growing obsession with locating the mythical source of this wealth.
When the lake failed to yield a golden metropolis, the search parties pushed deeper into the unforgiving Amazon rainforest. Expeditions marched blindly into the jungle, battling disease and hunger while chasing rumors of a civilization hidden behind the trees. Many explorers vanished without a trace, swallowed by the dense vegetation that guarded the secrets of the indigenous people. While they never found streets paved with gold, recent LiDAR scans suggest these adventurers might have walked right past complex ancient cities without realizing it. The true treasure was likely the sophisticated society itself, which remained hidden from European eyes for centuries.
LiDAR Technology Reveals a Hidden Civilization
For centuries, explorers hacked through dense vines looking for shimmering gold, but the real treasure was hiding in plain sight. In 2025, researchers finally peeled back the Amazon rainforest’s green curtain using advanced LiDAR technology. This laser mapping system shoots pulses from the sky to measure the ground below, effectively erasing the trees from the digital map. Instead of finding a single city paved with gold, the scans revealed a massive web of interconnected settlements. What looked like wild jungle was actually a sophisticated landscape shaped by human hands long before Europeans arrived.
The scale of this ancient civilization forces historians to rethink everything they knew about the Amazon. Detailed images show over twenty major urban centers linked together by miles of straight, raised roads and canals. These were not just scattered tribes, but a highly organized society capable of moving earth on a colossal scale. Researchers identified huge ceremonial plazas and geometric mounds that connect over twenty major sites. While the legends promised gold, the true engineering marvel implies a different kind of wealth based on agriculture and trade.
This discovery suggests that the El Dorado legend might have been a misunderstanding of a sprawling population rather than a specific location. Early Spanish conquistadors likely heard stories of these vast networks and twisted them into fantasies of infinite treasure. The Muisca people of Colombia practiced rituals with gold dust, but the real power lay in this newly mapped infrastructure. Science has finally caught up to the myths, proving that a lost civilization did exist, just not in the way anyone expected. As archaeologists prepare to dig deeper, one has to wonder what other secrets are still waiting under the canopy.
Uncovering the Amazon’s Hidden Civilization
The centuries-old search for a glimmering metropolis has shifted from a greedy treasure hunt to a groundbreaking scientific endeavor. Instead of finding a single city paved with gold, modern researchers using LiDAR technology have uncovered something far more valuable hidden beneath the dense jungle canopy. This recent discovery of a vast network of settlements proves that the Amazon was once home to a complex and thriving civilization. What was once dismissed as a fever dream of Spanish explorers is now reshaping history books and revealing the true ingenuity of pre-Columbian societies. The real treasure turned out to be the lost history of the people themselves rather than a pile of precious metal.
These findings suggest that the dense rainforest still guards countless secrets waiting for the right technology to bring them to light. With only a fraction of the Amazon Basin scanned by lasers, it is thrilling to imagine what other ancient wonders remain obscured by the thick vegetation. The transition from the myth of El Dorado to the reality of these engineered cities opens the door to even more mysterious possibilities. Perhaps other legends dismissed as folklore are actually rooted in forgotten historical truths that are just waiting to be found. We want to hear your perspective on these unfolding mysteries. Do you believe the Amazon holds even older civilizations, or are there other lost cities from legends that might actually exist?
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Where is the lost city of El Dorado located?
The legend places El Dorado deep within the South American jungles of the Amazon and the Andes mountains of present-day Colombia. While explorers searched for a specific city paved with gold, the true location centers around Lake Guatavita where the Muisca people performed their sacred rituals. Modern scans have recently identified a vast network of settlements hidden in this dense region.
2. Was El Dorado a real city paved with gold?
El Dorado was actually a person rather than a physical place. The name translates to “The Golden One” and refers to a Muisca tribal leader who covered himself in gold dust during a ceremony. Spanish conquistadors misunderstood this story and searched for a kingdom made of metal instead of a ruler.
3. What was the ritual of the Golden Man?
Historical records describe a chieftain covering his body in sticky resin and gold dust before diving into Lake Guatavita. He would then toss gold trinkets and emeralds into the water as offerings to the gods. This sacred tradition sparked the feverish treasure hunts that followed.
4. How did scientists find the lost settlements in 2025?
Researchers used advanced LiDAR technology to digitally strip away the layers of trees and vines. This laser scanning revealed a massive network of settlements, roads, and ceremonial plazas that had been invisible to the naked eye. It proves a sophisticated society thrived there long ago.
5. Why did explorers fail to find the city for centuries?
The Amazon rainforest is incredibly dense and dangerous, guarding its secrets with thick vegetation and difficult terrain. Explorers were looking for a shining city of gold that never existed in that form. They missed the real signs of civilization that were hidden beneath the jungle canopy.
6. Is there any actual gold in Lake Guatavita?
While there is no city paved with gold streets, the region held significant wealth for the indigenous people. Many gold artifacts and offerings were thrown into Lake Guatavita, some of which were recovered during early attempts to drain the lake. The true treasure was likely the complex civilization itself.
7. Who were the Muisca people mentioned in the legend?
The Muisca people inhabited the high Andes of Colombia and created a rich culture centered on a spiritual connection to nature. Recent scans show they built an interconnected society capable of surviving in a harsh environment. Their legacy is far more impressive than the simple myth of greed suggests.